“Effective Strategies to Control the Greenhouse Effect: Mitigating Climate Change and its Impact”

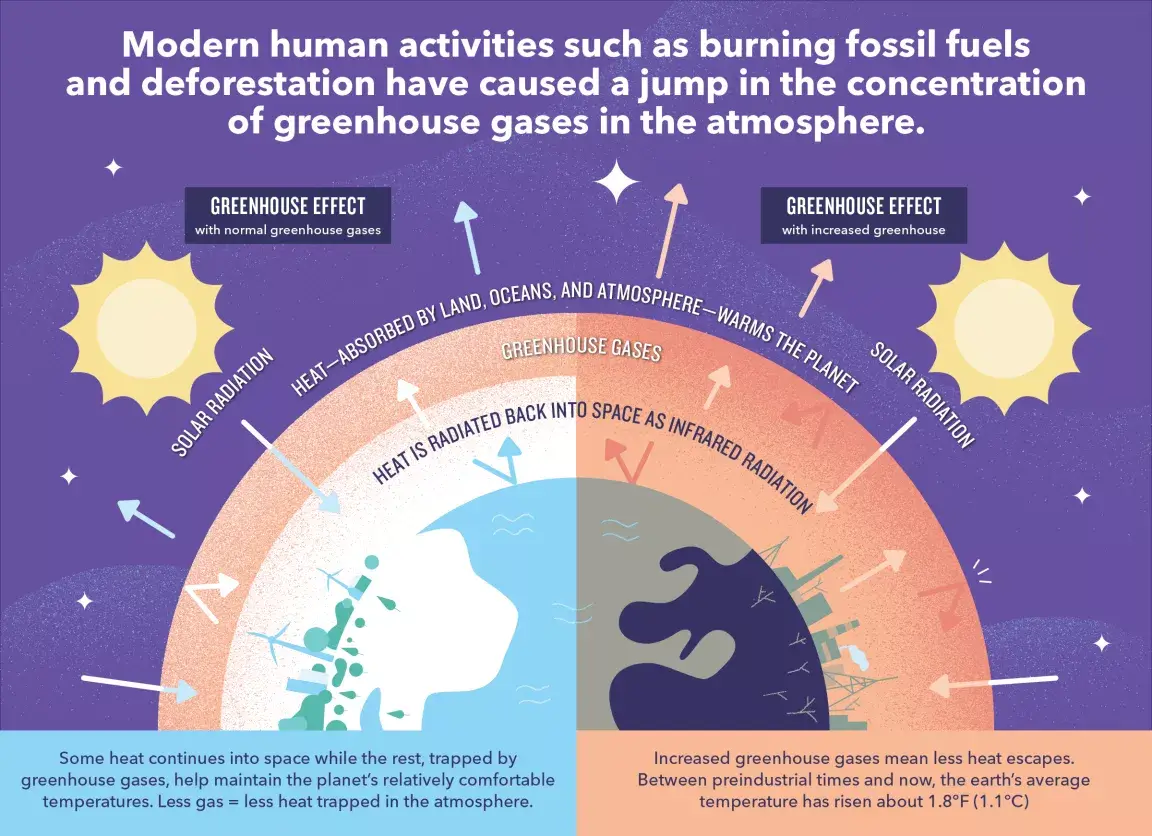
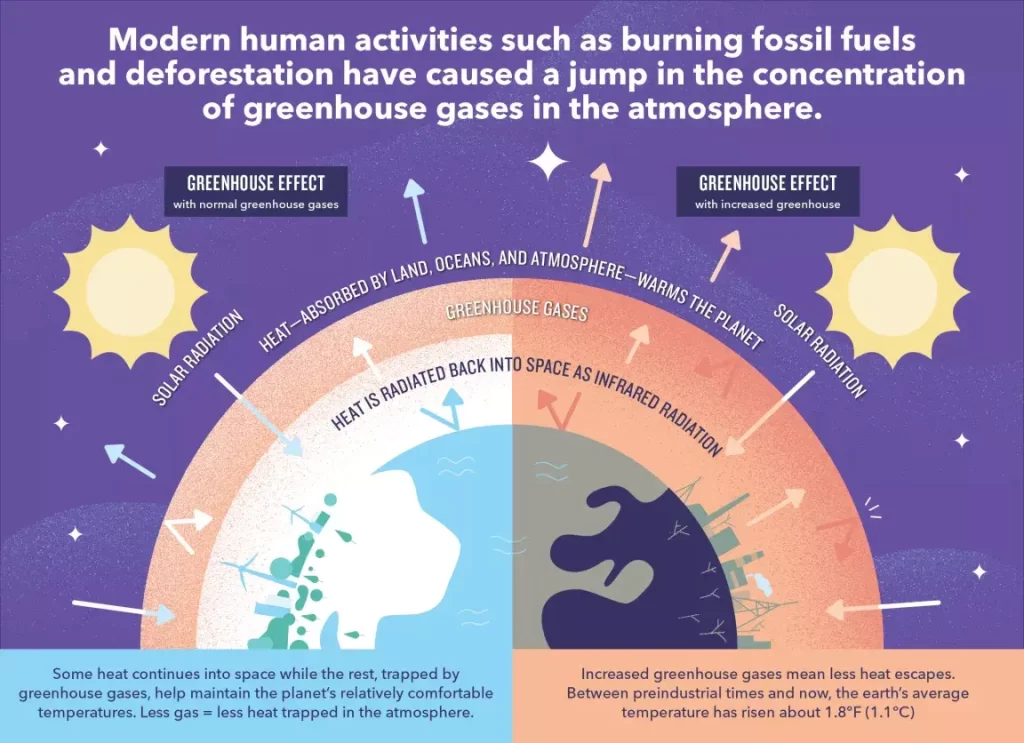
The Greenhouse Effect is a natural process that plays a crucial role in regulating the Earth’s temperature and making the planet habitable. It is named after a greenhouse, where sunlight enters through transparent windows and warms the interior, but the heat is trapped inside, leading to an increase in temperature inside the greenhouse.
In the Earth’s atmosphere, certain gases, known as greenhouse gases, act in a similar way to the transparent windows of a greenhouse. These greenhouse gases, such as carbon dioxide (CO2), methane (CH4), water vapour (H2O), nitrous oxide (N2O), and some others, allow sunlight (solar radiation) to pass through the atmosphere and reach the Earth’s surface. Once there, the Earth absorbs this solar radiation and then emits infrared radiation back into the atmosphere.
“Unlocking the Secrets of Global Warming: Understanding, Impacts, and Solutions”
Greenhouse gases in the atmosphere absorb some of this infrared radiation and re-emit it in all directions, including back towards the Earth’s surface. This process effectively traps some of the heat within the Earth’s atmosphere, preventing it from escaping into space. As a result, the Earth’s average temperature is higher than it would be without the greenhouse effect, making the planet suitable for life as we know it.
The greenhouse effect is a natural phenomenon and has existed for billions of years. However, human activities, such as burning fossil fuels (coal, oil, and natural gas), deforestation, industrial processes, and agriculture, have significantly increased the concentration of greenhouse gases in the atmosphere. This enhanced greenhouse effect is commonly referred to as “anthropogenic global warming” or “climate change.”
The excessive release of greenhouse gases has intensified the greenhouse effect, leading to an imbalance in the Earth’s climate system. This imbalance causes global temperatures to rise, leading to various consequences like melting glaciers, rising sea levels, more frequent and severe extreme weather events, and disruptions to ecosystems and agriculture.
Efforts to address the greenhouse effect and its impacts involve strategies to reduce greenhouse gas emissions, transition to renewable and cleaner energy sources, enhance energy efficiency, protect and restore forests, and implement various climate policies and agreements on a global scale. The goal is to mitigate the effects of climate change and reduce the risks posed by its consequences to human societies and the environment.
Effects of the Greenhouse Effect
The effects of the greenhouse effect can be both natural and anthropogenic (human-induced). While the natural greenhouse effect is necessary to maintain a stable and habitable climate on Earth, the anthropogenic enhancement of this effect is leading to significant environmental and climatic changes. Here are some of the key effects of the greenhouse effect:
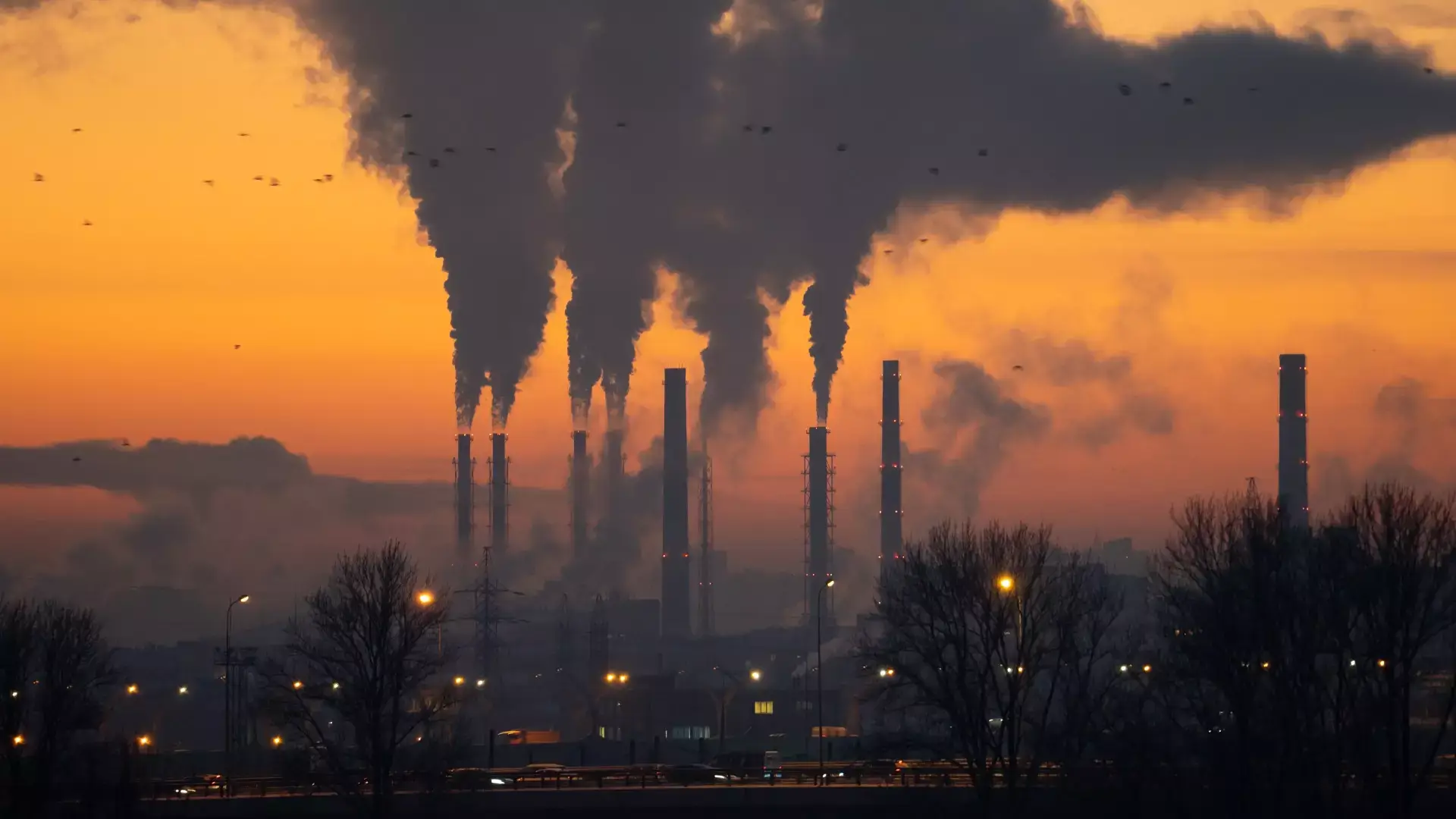
- Global Warming: The primary consequence of an intensified greenhouse effect is global warming. As more greenhouse gases accumulate in the atmosphere due to human activities, they trap more heat, leading to an overall increase in the Earth’s average temperature. This warming trend has been observed over the past century and is linked to the burning of fossil fuels, deforestation, and other human activities.
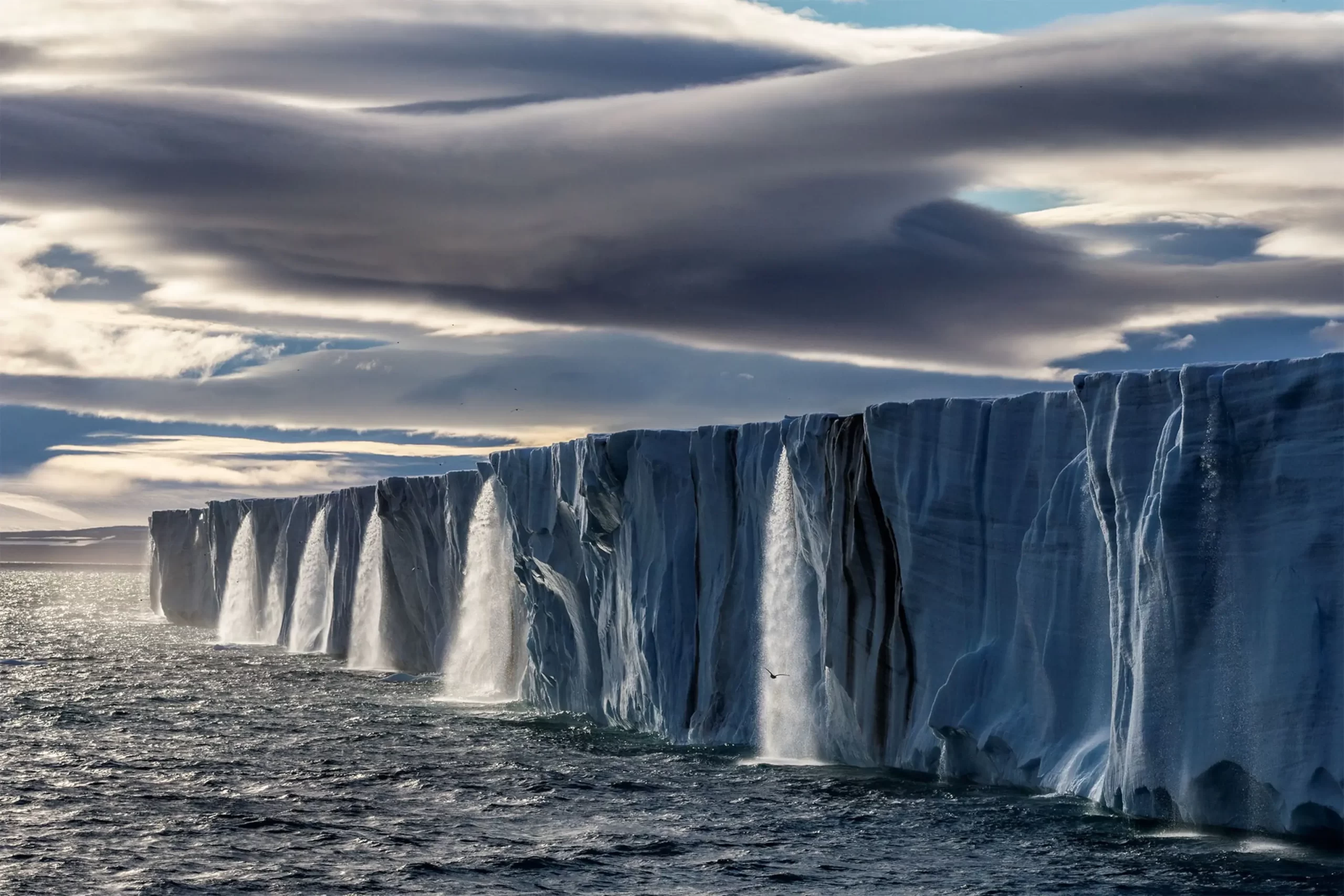
- Melting Ice and Rising Sea Levels: The increase in global temperatures causes glaciers and ice sheets in polar regions to melt at an accelerated rate. As a result, there is a net loss of ice mass from polar ice caps, leading to rising sea levels. This phenomenon poses a threat to low-lying coastal areas, islands, and densely populated coastal cities, making them vulnerable to flooding and erosion.
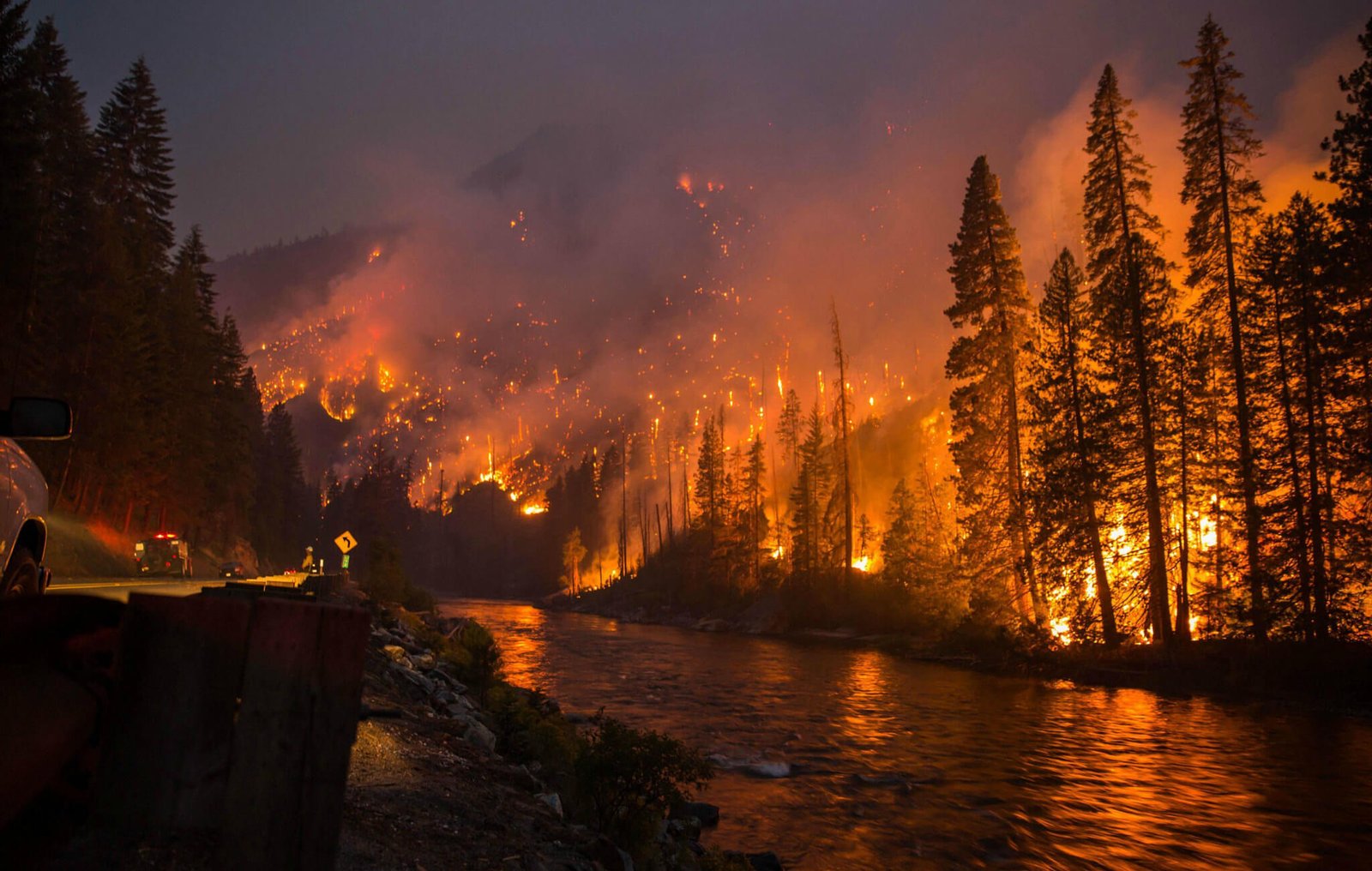
- Extreme Weather Events: Global warming intensifies certain weather patterns and leads to an increase in the frequency and intensity of extreme weather events. This includes heatwaves, hurricanes, typhoons, heavy rainfall events, and droughts, which can have devastating impacts on communities, agriculture, and ecosystems.
- Ocean Acidification: The excess carbon dioxide in the atmosphere is not only affecting the atmosphere but also being absorbed by the oceans. This causes the oceans to become more acidic, a process known as ocean acidification. Ocean acidification can harm marine life, especially organisms like coral reefs, shellfish, and plankton with calcium carbonate shells or skeletons.
- Disruption of Ecosystems: Climate change resulting from the greenhouse effect can lead to disruptions in ecosystems and biodiversity. Many species may struggle to adapt to rapidly changing environmental conditions, leading to shifts in ecosystems, loss of biodiversity, and potential extinction of some species.
- Agriculture and Food Security: Changes in temperature and precipitation patterns can affect agricultural productivity and food security. Some regions may experience reduced crop yields, while others may become more suitable for certain crops. These shifts can have both positive and negative impacts on regional and global food production.
- Health Impacts: The increasing frequency and intensity of heat waves can pose health risks, particularly for vulnerable populations, such as the elderly, young children, and people with pre-existing health conditions. Additionally, changes in the distribution of disease vectors, such as mosquitoes, can lead to the spread of diseases like malaria and dengue fever to new regions.
- Economic Consequences: The effects of greenhouse effect can have significant economic impacts, including increased costs for infrastructure repairs and adaptation measures, potential loss of property and assets due to sea-level rise and extreme weather events, and changes in the availability and pricing of natural resources.
To mitigate the adverse effects of the greenhouse effect, it is essential to take measures to reduce greenhouse gas emissions, transition to renewable and cleaner energy sources, promote sustainable land use and forest management, and implement global climate policies and agreements. International efforts, such as the Paris Agreement, aim to address climate change and limit global warming to well below 2 degrees Celsius above pre-industrial levels to avoid the worst consequences of the greenhouse effect.
Strategies to help control the greenhouse effect:
Controlling the greenhouse effect and mitigating its impacts involves a combination of individual, local, national, and international efforts. Here are some key strategies to help control the greenhouse effect:
Reduce Greenhouse Gas Emissions:
a. Transition to Renewable Energy: Increase the use of renewable energy sources such as solar, wind, hydro, and geothermal power to replace fossil fuels in electricity generation and transportation.
b. Improve Energy Efficiency: Implement energy-efficient technologies and practices in industries, buildings, and transportation to reduce energy consumption and emissions.
c. Carbon Capture and Storage: Develop and implement technologies to capture and store carbon dioxide emissions from industrial processes and power plants.
d. Reduce Deforestation: Protect and restore forests, as trees absorb carbon dioxide and help offset greenhouse gas emissions.
e. Sustainable Agriculture: Encourage sustainable agricultural practices that reduce methane emissions from livestock and rice paddies, and promote low-carbon farming techniques.
Promote Climate-Friendly Policies:
a. Carbon Pricing: Implement carbon pricing mechanisms such as carbon taxes or cap-and-trade systems to incentivize businesses and individuals to reduce their carbon footprint.
b. Renewable Energy Incentives: Provide financial incentives and subsidies for the adoption of renewable energy technologies to accelerate the transition away from fossil fuels.
c. Environmental Regulations: Enforce and strengthen regulations on emissions from industries, transportation, and other sectors to limit greenhouse gas pollution.
d. Support Climate Research: Invest in research and development to advance technologies and practices that can help address climate change effectively.
Enhance International Cooperation:
a. Paris Agreement: Support and comply with international agreements like the Paris Agreement, which aims to unite countries in their efforts to limit global warming and its impacts.
b. Global Partnerships: Collaborate with other countries and organizations to share knowledge, resources, and best practices for climate change mitigation.
c. Climate Diplomacy: Engage in diplomatic efforts to encourage global action on climate change and promote sustainable development.
Best Antivirus Programs that Will Keep Your PC Safe in 2023
Foster Sustainable Lifestyle Choices:
a. Energy Conservation: Encourage individuals to reduce energy consumption in their homes and workplaces through energy-saving habits and using energy-efficient appliances.
b. Public Transportation: Promote public transportation and active transportation options (e.g., walking and cycling) to reduce reliance on fossil fuel-powered vehicles.
c. Waste Management: Implement effective waste management practices, including recycling and waste reduction, to minimize methane emissions from landfills.
Educate and Raise Awareness:
a. Public Awareness Campaigns: Raise awareness about climate change, its impacts, and the importance of individual and collective actions in addressing it.
b. Environmental Education: Incorporate climate change and sustainability education into school curricula to empower the younger generations with knowledge and a sense of responsibility.
Controlling the greenhouse effect is a global challenge that requires collective action from governments, businesses, communities, and individuals. By working together and implementing these strategies, we can take significant steps toward a more sustainable and climate-resilient future.









These are truly great ideas in regarding blogging. You have touched some pleasant points here.
Any way keep up wrinting.
[…] […]
[…] […]
[…] […]
Just a smiling visitant here to share the love (:, btw great style.